|
|
GeoAstro Applets |
Astronomy |
Chaos Game |
Java |
Miscel- laneous |
Physics Quiz |
Who is Who ? |
|
Planet Applet Applet Details Planetary Events Solutions |
|
|
|
Planet Applet: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and the Moon |
|
|
|
|
|
value derived from longitude: |
|
|
Enter latitude in decimal degrees and press return
key, |
 |
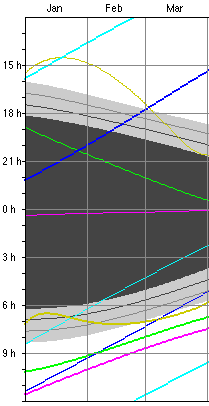
1. a Diagram showing the rise and set times over the
year, 3 different representations |
 |
Use the Planets, Moon menu items to show or hide the planets and the Moon. |
 |
The items of the Details menu,
working in toggle mode, show and hide additional
details. |
|
|
You may use the keys y, m, w, d, h, n to
increase the yaer, month, week,date, hour, or
minute, Use c or shift key and c
to increase/decrease the century. |
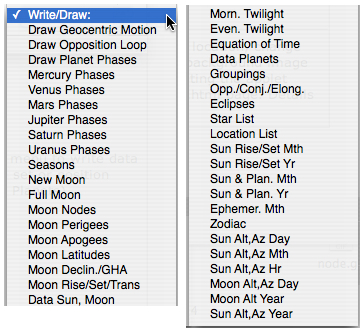 |
Choose from the Write/Draw ... menu to write data to a new window |
|
|
You may enter your home location by editing the applet parameters of this HTML page. Details here. |
In case the applet is not running, click here
Planetary events to discover and to explore
1. Select "Diagram" from the View menu:
Redrawing the diagram will take some time because of 365 complex computations have to be done.
To
draw rise and set of a single planet select "None" from the Planets,
Moon menu
and then turn on the planet to show.
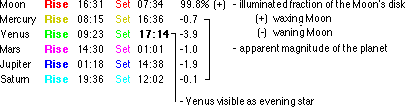
Example: Berlin, 2004 March 20:
![]()
Rise Set
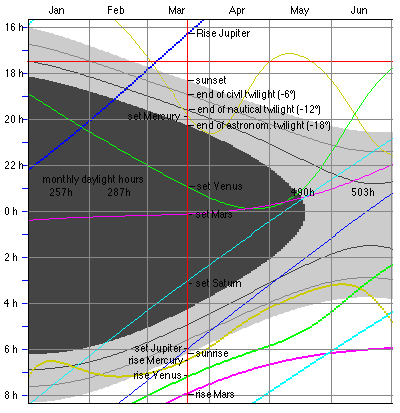
There
are
three different representations of the diagram: ![]()
 |
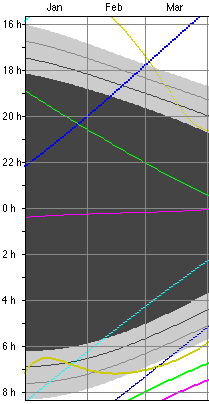 |
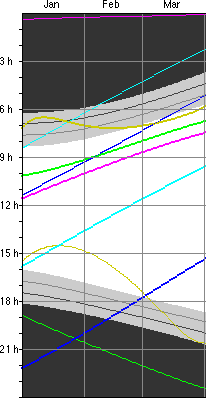 |
|
|
|
|
To hide or show the current sun in the Diagram View choose "Sun" from the "Details" menu.
To
show the visibility of a planet select "None" from
the "Planets,Moon" menu,
and than the planet.
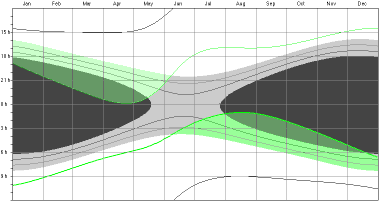
2004: Venus visible as Evening Star (upper green regions)
or Morning Star (lower regions)
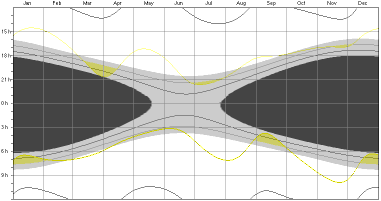
2004: Visibility of Mercury
|
|
The duration of the Astronomical Night |
2. Select "Horizon Rectang." from the View menu:
![]()
This
equirectangular
projection is a cylindrical equidistant projection,
in which the horizontal coordinate is the longitude and the
vertical coordinate is the latitude. (x=λ, y=φ, equator as
standard parallel).
Extreme distortions near the poles.
To draw the diurnal path of the Sun select "Show Orbits" from the "Planets, Moon" menu.
3. Select "Horizon Spher." from the View menu:
![]()
|
|
You may use the keys m, w, d, h, n to increase
the month, week, date, hour, or minute |
|
|
|
Use the Planets, Moon menu items to show or hide the planets and the Moon. |
|
|
|
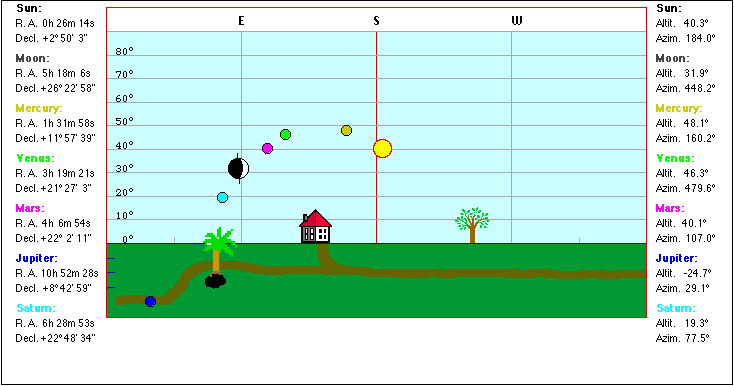
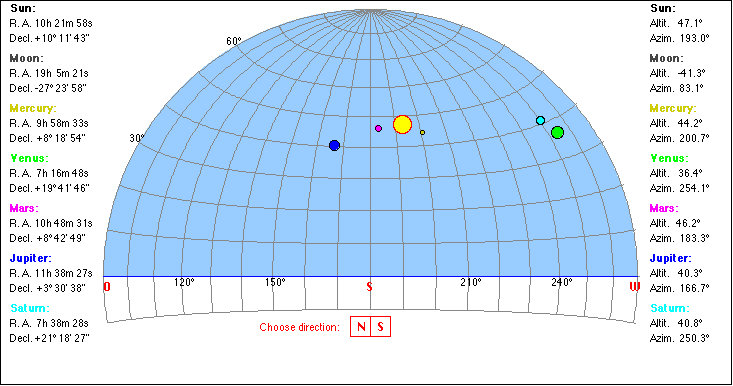
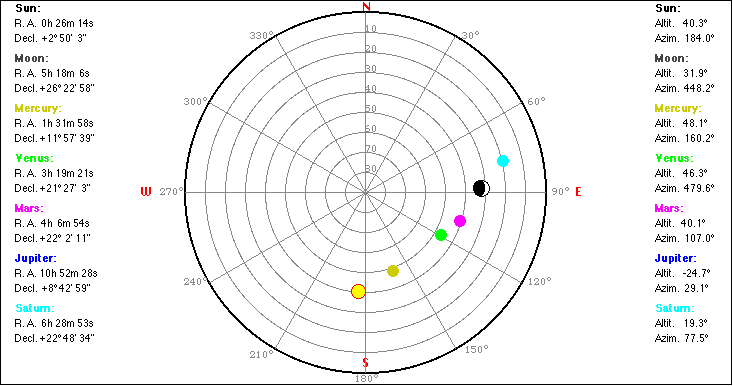
Click a celestial body to read its azimuth and elevation. |
|
 |
The items of the Details menu,
working in toggle mode, show and hide additional
details (if applicable). |
|
|
|
magnitudes of planets |
|
|
|
Altitude (Elevation) Azimuth |
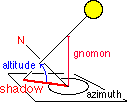 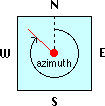 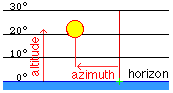 |
|
|
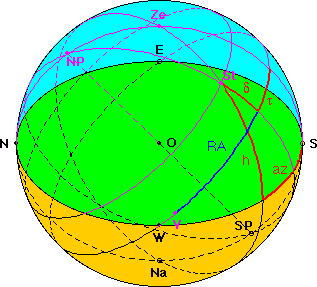
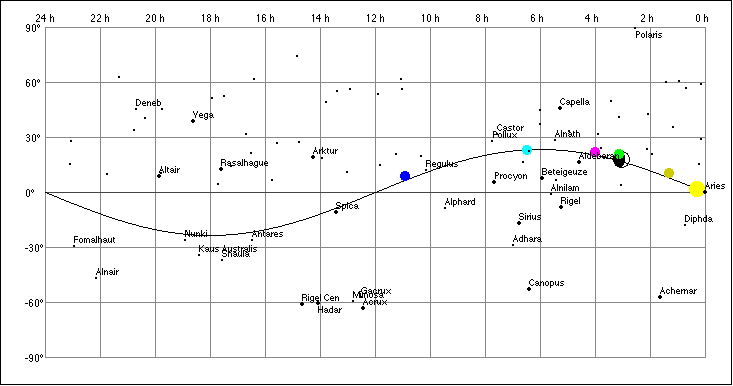
Right Ascension Declination The first equatorial coordinate of a star (St) is the declination delta, measured in degrees north and south of the celestial equator (N: 0° < delta < 90°, S: 0° > delta > - 90°. The second coordinate is the Right Ascension RA, measured along the equator from from a zero point known as the vernal equinox (V). |
A screen shot of Walter Fendts applet |
 |
-6° < elevation < 0° -12° < elevation < -6° -12° < elevation < -18° elevation < -18° |
civil twilight nautical twilight astronomical twilight |
|
|
The Julian Day and the Local Mean Sidereal Time are indicated. |
|
 |
|
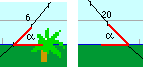
Select "Sun" from "Choose Details" to see the path of the Sun, and the intersection angle with the horizon (alpha). By this angle the time interval for rise and set is computed (in minutes): 4*sunDiameter/sin(alpha) |
4. Select "Horizon Polar" from the View menu:
![]()
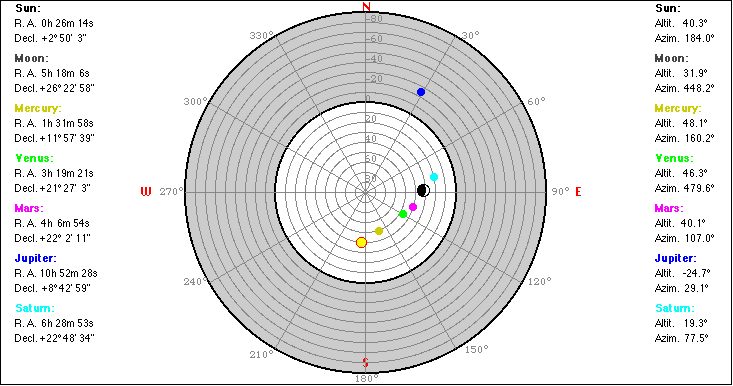
or "Horizon Pol. Zoom":
![]()
you
may
choose details: 
To draw the diurnal path of the Sun select "Show Orbits" from the "Planets, Moon" menu.
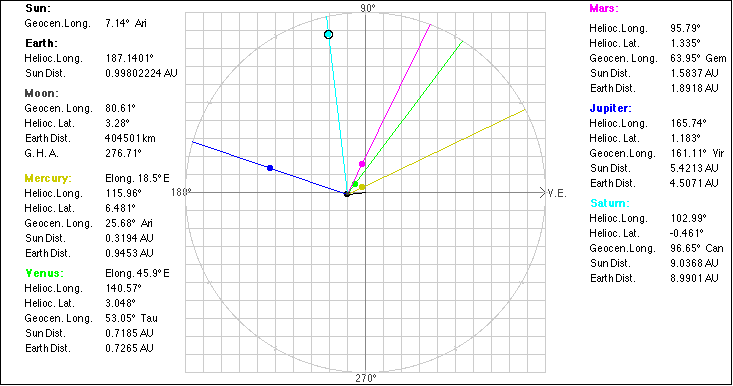
5. Select "Ecliptic" from the View menu:
![]()
(from above the solar north pole)
or Select "Ecliptic Zoom":
![]()
(not showing Jupiter and Saturn)
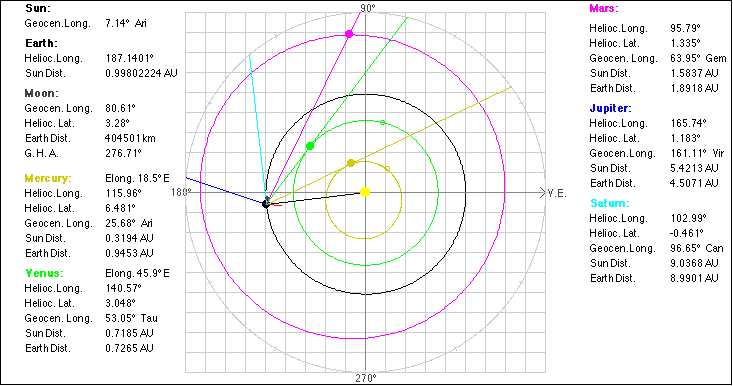
Ascending node, the point where the
planet crosses the ecliptic from south to north.
Perihelion (Perigee), the point of
closest approach to the Sun. Aphelion (Apogee), the point furthest
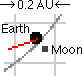
from the Sun. The Earth-Moon distance is magnified by
25. The red line is the Greenwich meridian.
Use the keys commands h, d, w,
m to increase the hour, date, or month, to
observe retrograde motion. Use the "Planets, Moon" menu to show or
hide the Earth-Planet lines and the orbits.
For Mercury and Venus the current
elongation angle from the Sun is displayed. The opposition or conjunction of a
planet is indicated in case the proper month and
date is selected. The planet is above the ecliptic plane The planet is below the ecliptic plane
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
An eastern elongation angle
means Mercury will be visible in the western sky
after sunset, while for a western elongation
Mercury is visible in the eastern sky before dawn.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
(heliocentric latitude is positive).
(heliocentric latitude is negative)
![]()
6. Select "Ecl. Earth/Moon" from the View menu:
![]()
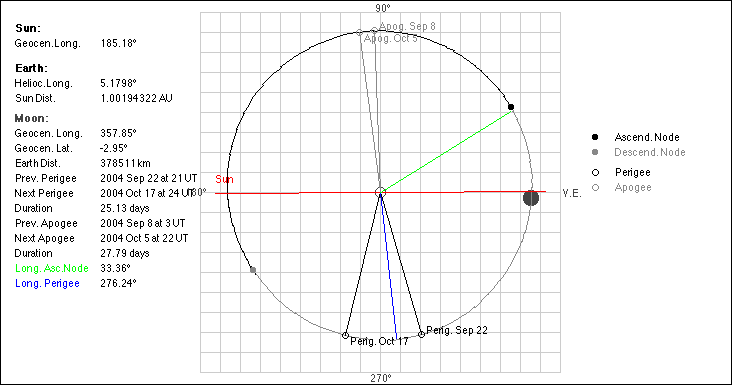
To switch off the lines choose "Hide Lines" from the "Planets, Moon" menu.
Watch
the
retrograde rotation of the (green) line of nodes (the mean longitude
decreases by about 19° per year),
and the prograde rotation of the (blue) line of perigee (the mean longitude
increases by about 41° per year).
Lunar Perigee and Apogee Calculator
Applet: Computing the motion of the Moon
7. Select "Sky Map" from the View menu:
![]()
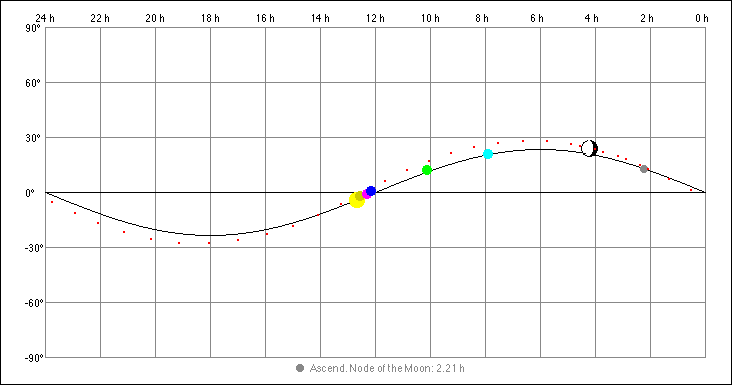
The ascending node of the Moon is
indicated (grey oval). The example is showing a loop of Mars
(retrograde motion). Click the sky map to show the
coordinates. Command key and click
will draw a green cross mark. These coordinates
(RA and decl.) are indicated in the "Horizon
Rectang.", in the "Horizon Polar", and in the
"Horizon Spher." view:
Choosing "Show Path" from the "Choose Details"
menu will draw the positions of the Moon for the
current month and of the planets around the
current date:
+/-45 days for Mercury, Venus,
+/- 90 days for Mars, Jupiter,
+/- 120 days for Saturn.
![]()
or
choose:

Use "Stars and Names" from the Details menu to show or hide star names.
Click
a
star to show its name and magnitude: ![]()
8. Select "Earth Map" from the View menu:
![]()
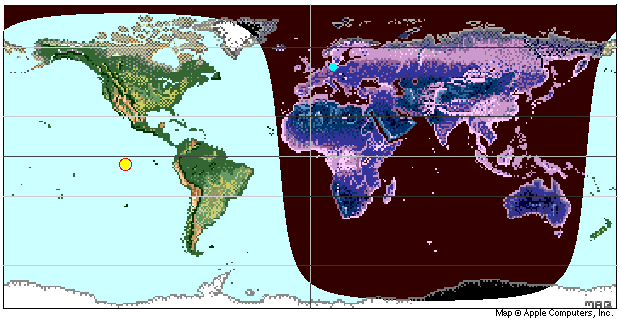
Use the Details menu to add more details (stars, bright planets, etc.):

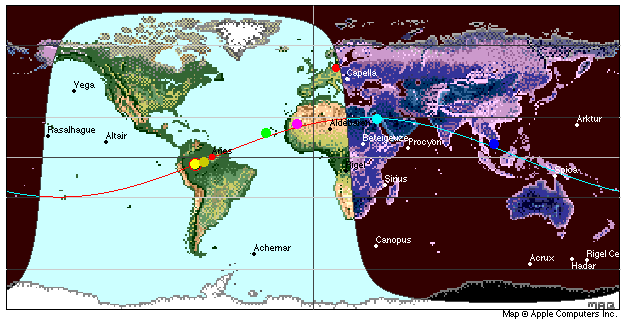
A
celestial bodies (star, planet) is seen at the zenith by an
observer
located at the position of the body on the world map
(declination=latitude, hour angle=longitude).
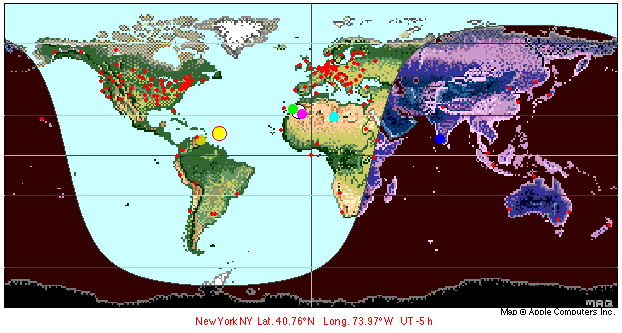
Click
the
map to get the location, or the latitude and longitude
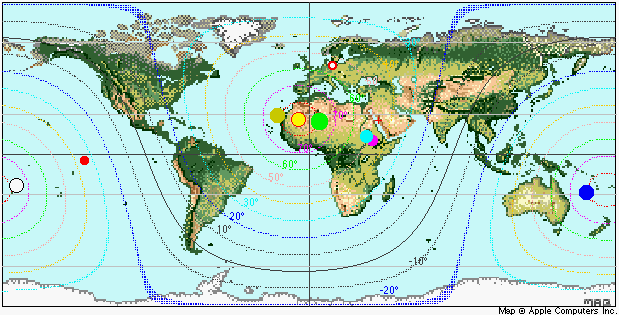
Select
"Altitudes
Sun" from the details menu to draw lines of equal Sun
altitudes
Data and Graphics windows:
Choose
from
the Write/Draw ...
menu
Dates of New Moon and Full Moon for the
year selected, and lunations. Local Full Moon Transit Elevation Dates and times of the node passages of
the Moon. Dates and times of the perigees or
apogee of the Moon. Anomalistic
Month Extreme ecliptic latitudes of the Moon (diagram) Extreme declinations of the Moon (diagram) The window "Data Sun and Moon" :
- the date and time of solstices,
equinoxes, perihelion and aphelion for the current
year. - the date and time of New and Full Moon
for the current month (UT is accurate within +/-1
hour). - the date and time of the Moon's
perigee and apogee for the current month. The hours (UT) are accurate within +/-1
hour). Table showing the begin (end) of
nautical and civil twilight (depression 6°), the
sunrise (sunset), and the duration of civil and
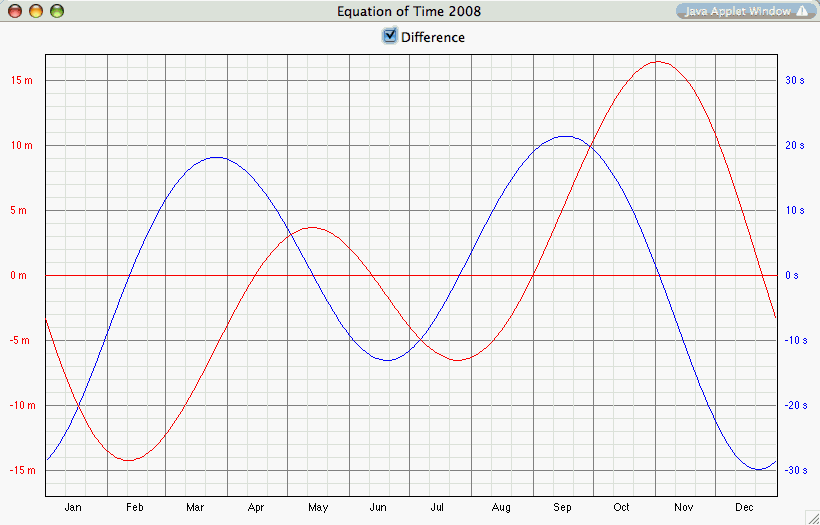
nautical twilight. List of the Equation of Time (at 12 UT)
and the daily change. Perigee, Apogee Planetary separations (in geocentric
longitude) of less than 5° (or 10°, or 3° when
opened again) taking place more than 10° from the
Sun. Opposition, conjunction, Lunar Eclipses: The brightest stars (mag<2), and
their rise, transit, and set time. The locations available from the
Location menu. Sunrise and sunset, civil, nautical, and
astronomical twilight, daylight hours. Sunrise and sunset, civil, nautical, and
astronomical twilight, daylight hours Sun & Plan Month Sunrise and sunset, civil, nautical, and
astronomical twilight, daylight hours, Positions at 0:00 UT: Sun Alt & Azim Day Altitude and azimuth of the sun for the
date selected. Altitude and azimuth of the Moon for the
date selected. Altitude of the Moon at transit for the
location and year selected.
Draw
Geocentric Motion
Draw
Opposition
Loop
Draw
Equation of Time
Draw Planet Phases
Draw diagrams:

Create a table
of the dates of conjunctions and phases.
Synodic Month
(diagram)
Draconic Month
Moon
Alt/Az/Phase
Altitude,
azimuth and illuminated fraction of the Moon for any
day of the month selected (1 hour interval).
The mean error is less than 1 second.
node passages (ascending, descending).
max. Elongations of Mercury and Venus.
looking for Full Moon (difference of geocentric
longitudes 180°, opposition) and ecliptic latitude
<+/-1.5°
Solar Eclipses:
looking for New Moon (difference of geocentric
longitudes 0°, conjunction) and ecliptic latitude
<+/-1.5°
details about daylight hours, latest sunrise, and
earliest sunset.
Sun & Plan Yr
rise and set of the planets and the Moon.
Apparent Heliocentric Position: longitude,
latitude, distance.
Apparent Geocentric Positions (True Equinox
and Ecliptic of Date)
Ecliptic System: longitude, latitude,
and Equator System: right ascension, declination,
distance,
errors: longitude +/- 0.01°, latitude +/- 0.001°.
Compare
with MICA (Multiyear
Interactive Computer Almanac, U.S. Naval
Observatory)
Zodiac
the Position of
the Sun, Moon and planets
Sun Alt & Azim Hr
(diagram)
Geocentric
Motion:
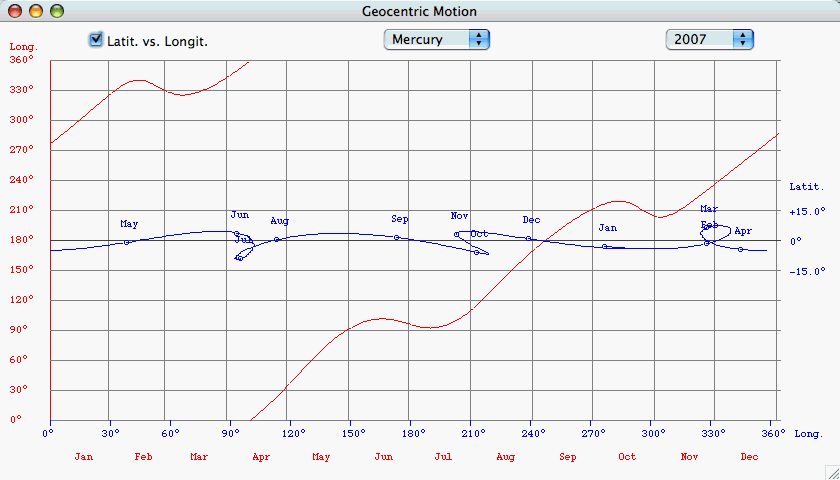
Details for
the opposition loops of Mars
Retrograde
motion
is
occurring
for the outer planets at their opposition,
and for the inner planets at inferior conjunction.
![]() Planetary Phenomena
Planetary Phenomena
![]() Eclipse Home Page (Fred Espenak)
Eclipse Home Page (Fred Espenak)
APPLET Parameters:
You
may
enter your home location and change some settings by editing
the applet parameters of the HTML page.
Open "index.html" in Netscape's Composer, in any HTML editor
or in Windows' editor.
|
<APPLET CODE="planets113.class"
WIDTH=780 HEIGHT=580 ALIGN=bottom
archive="applet/JavaClasses.jar"> |
Do not change. |
|
<PARAM NAME=location VALUE="Berlin"> <PARAM NAME=latitude VALUE="52.51"> <PARAM NAME=longitude VALUE="13.41"> |
Edit the text of the location parameter, and the values of the latitude and
longitude parameters (decimal degrees). |
|
<PARAM NAME=background VALUE=0> |
Set the background parameter value
to 1 |
|
<PARAM NAME=image VALUE=sunview> |
Change the image parameter value
to sunview1 |
|
<PARAM NAME=startview VALUE=2> |
Set the startview parameter value
to |
|
</APPLET> |
|
© 2003-2014 J. Giesen