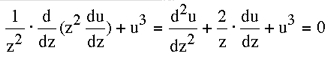|
|
GeoAstro Applets |
Astronomie |
Chaos Spiel |
Java |
Diverses |
|
Wo jetzt
nun, wie unsre Weisen sagen,
Seelenlos ein Feuerball sich dreht, Lenkte damals seinen goldnen Wagen Helios in stiller Majestät. aus Friedrich Schillers Gedicht "Die Götter Griechenlands" The Standard
Stellar Model Emden's
differential equation arising in the study of
stellar interiors assuming a polytropic model
(constant K, polytropic index n=3) is given by:
u is a (dimensionless)
temperature, the (dimensionless) variable z is
related to the distance r from the center.
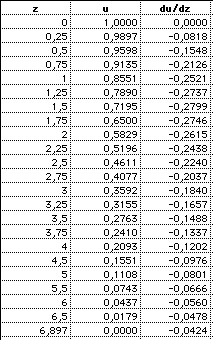
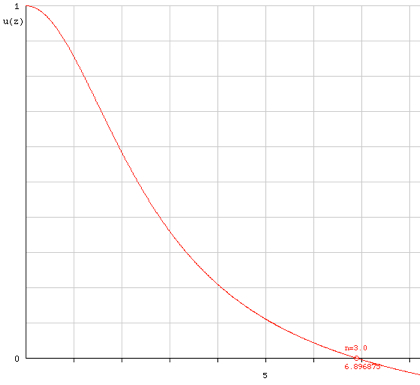
The solution can only be
obtained numerically by my Lane-Emden applet:
Tools: ODE
Toolkit (online), Berkeley
Madonna (Mac, Windows trial). The first zero of u(z) is
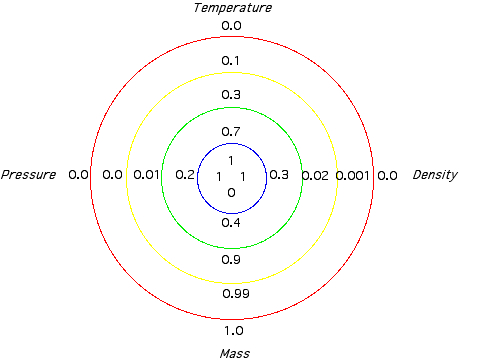
found to be z0=6.897. The relative distance is
r/R=z/z0. My results for the
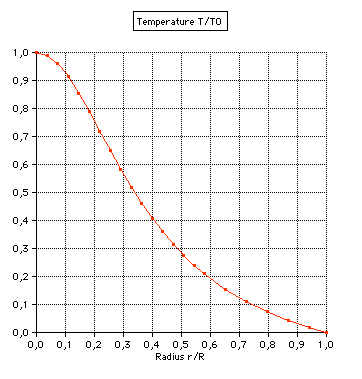
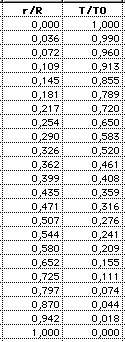
variables temperature, density, pressure, mass: (1) Temperature: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
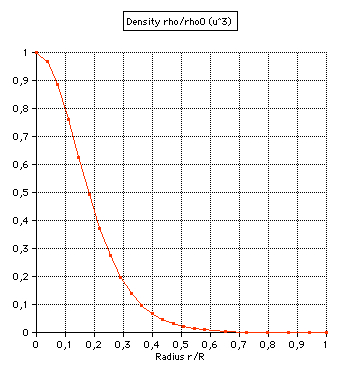
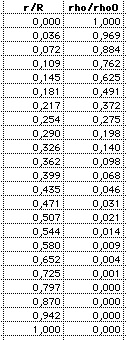
(2) Density: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
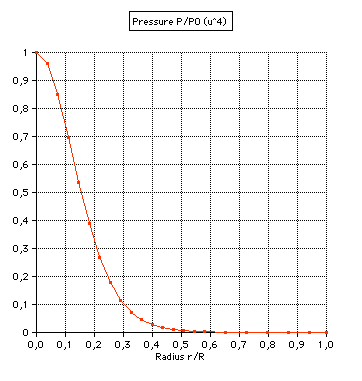
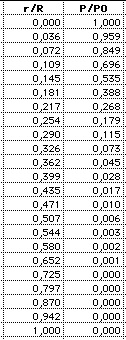
(3) Pressure: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
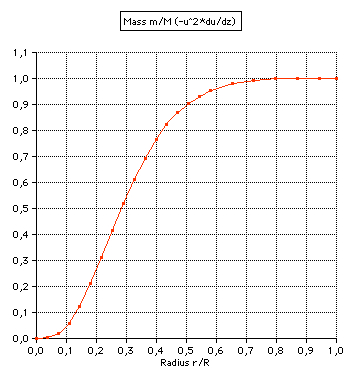
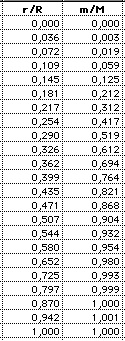
(4) Mass: m(r)/M is the fraction of the
total mass within the radius r. About half of the
mass is included by the sphere of radius r=0.3*R
(2,7% of the total volume).
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Relations of the standard model for the core values: 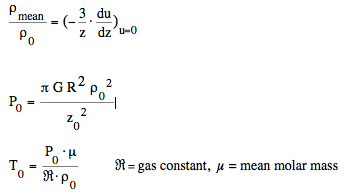 The
Sun:
Using the mass fractions
for the solar composition (Hydrogen x=0.734,
Helium y=0.25, heavier elements: 1-x-y = 0.016)
the mean molar mass, relative to hydrogen, is:In
case of complete ionisation:
μ
= 0.60114
or, in absolute units: μ = 0.60114 · 1.0079·10-3 kg/mol = 6.059·10-4 kg/mol The results for the Sun (polytropic index n=3): 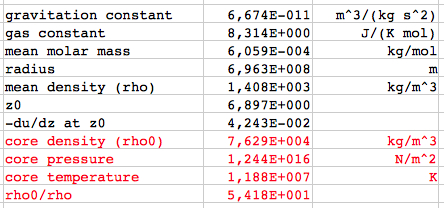 The results for the Sun (polytropic index n=2): 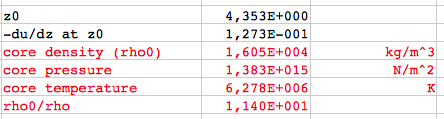 The results for the Sun (polytropic index n=4): 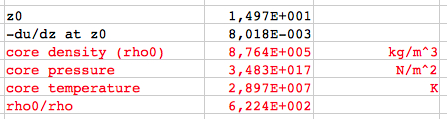 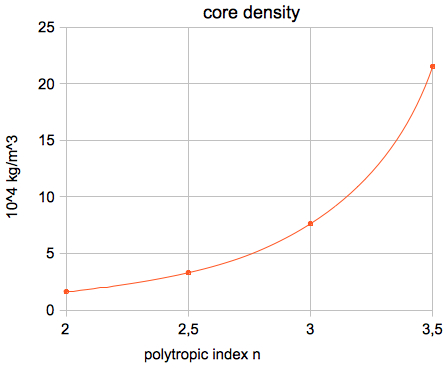 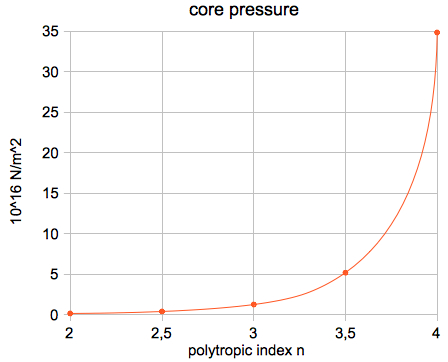 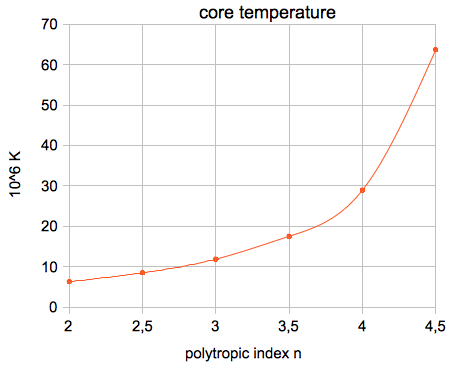 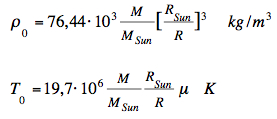 which agree very well with the
results of my applet.
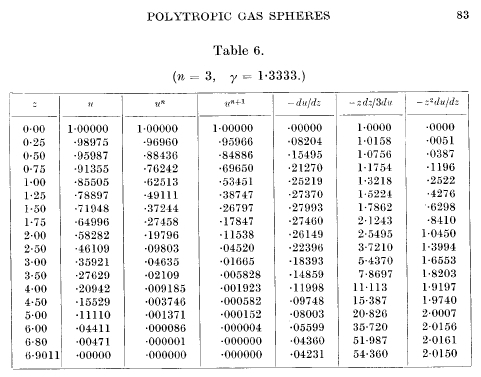 Table from the book of Eddington "The
successive colums give the following physical
quantities, expressed in each
case in terms of a unit which will depend on the star considered: 1. Distance from the centre. 2. Gravitational potential. Temperatute (for a perfect gas of constant molecalar weight). 3. Density. 4. Pressure. 5. Acceleration of gravity. 6. Reciprocal of mean density to the point considered. 7. Mass interior to the point considered." Using the symbols g, M, and R for the values at the surface (columns 5, 7, 1): g = acceleration of gravity = - du/dzwe have the relation (a): which
is Newton's law of gravitation
with gravitational constant
G=1 in units of the Lane-Emden equation.
The mean density (column 6) is (b): 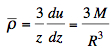 From (a) and (b):
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Lane-Emden
equation (wikipedia) Lane-Emden
Differential Equation (Wolfram MathWorld) Program
to
solve
the
Lane-Emden
equation numerically Lane, Jonathan Homer (wikipedia) Emden,
Robert (wikipedia) Stellar
Structure
and the Lane-Emden Function Lecture
23: The Lane-Emden Equation Polytropes
- Derivation and Sulution of the Lane-Emden
Equation Lane-Emden
Equation in Stellar Structute (Wolfram
Demonstrations Project)
|
|
|
A. S. Eddington: The Internal Constitution of the Stars, Cambridge University Press, 1926. H. Vogt: Aufbau und Entwicklung der Sterne, Akadem. Verlagsgesellschaft, Leipzig 1957. Robert Emden: Gaskugeln: Anwendungen der mechanischen Wärmetheorie auf kosmologische und meteorologische Probleme. Leipzig, Berlin: Teubner, 1907. Amazon: Books on Demand, ISBN 978-5875749025 Dermott J. Mullan: Physics of the sun: A First Course; CRC Press, Boca Raton - London - New York, 2009; ISBN 978-1420083071 https://www.crcpress.com/Physics-of-the-Sun-A-First-Course/Mullan/9781420083071 |
Last update: 2023, Oct 07
![]()