|
George Johnstone Stoney (1826 - 1911) By combinations of Newton's gravitation constant G, the velocity of light c and the electric charge of the electron e, Stoney could construct a mass, a length and a time, using the cgs system of units (1 cm, 1 gram, 1 second): 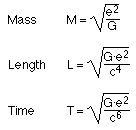 Using modern values (NIST), G = 6.674·10-8 cm3 g-1 s-2 c = 2.998·1010 cm s-1 we get Length L = 1.38·10-34 cm Time T = 4.60·10-45 s We can imagine the quantity of mass, but the length and the time are not corresponding to anything of our physical world. action = energy·time = M·L2 / T =
M·L·c = e2 / c Planck constant h = 6.626·10-34 Js
cgs System of Units Using cgs units Coulomb's law is The unity of charge (1 esu, 1 electrostatic unit) is defined as the charge on each of two bodies separated by 1 cm and attracting each other by a force of 1 dyne (1 dyne = 1 g cm s-2 = 1·10-5 N). Taking q1=q2=q and q2 = F r2 , we get To convert the electrostac unity (1 esu) to Coulomb (1 C), the the unity of charge of the SI system, we use Coulomb's law and q2 = 4πε0 F r2
We get: e = 1.602·10-19 C = 4.803·10-10 esu = 4.803·10-10 g1/2 cm3/2 s-1
George Johnstone Stoney : 1826 - 1911 Fundamental Quantum Cosmological Units and the Quantum
Evolution of the Universe Natural Systems of Units. To the Centenary Anniversary
of the Planck System (pdf) Trialogue
on the number of fundamental constants (pdf) John D. Barrow: Das 1x1 des Universums. Campus Verlag,
Frankfurt/New York, 2004. John D. Barrow: The Constants of Nature. Jonathan Cape,
2002. |
Juergen Giesen
2009/9/10