|
|
GeoAstro Applets |
Astronomy |
Chaos Game |
Java |
Miscel- laneous |
Ancient Theories of the Sun:
1. Eccentric Model Applet
3. Eccentric and
Equant Model Applet
 |
Select from
the Details menu. |
 |
Select the time interval. |
 |
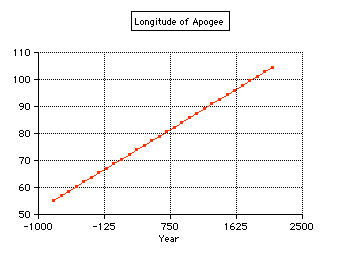
The angular
position of the apogee of the Sun is slowly moving
with time (about 1.71° per cencury, this is not the
precession of the equinoxes). |
|
There are
two mathematically
equivalent models of ancient Greek
astronomy explaining the unequal motion of the Sun:
|
|
|
Apogee A 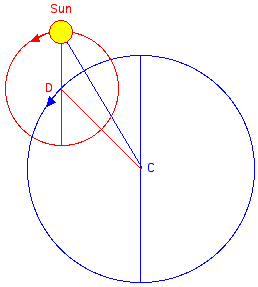 P Perigee |
Apogee A 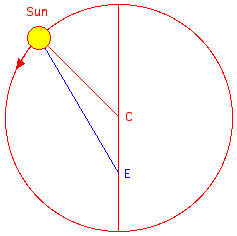 P Perigee |
| The
Sun moving on the epicycle
with center D rotating on the
deferent circle (center C) at the
same angular speed. e = distance from D to Sun rMin=r-e, rMax=r+e eccentricity=(rMax-rMin)/(rMax+rMin)=e/r |
The
Sun moving on the circle (radius r) centered at C seen
from the eccentric
point E. e = CE rMin=EP, rMax=EA eccentricity=(rMax-rMin)/(rMax+rMin)=e/r |
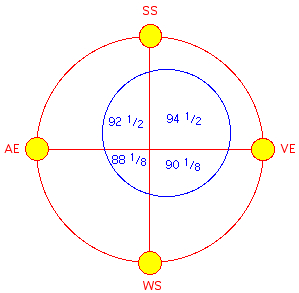
Lenghts
of the seasons:
|
|
Ptolemy (90 AD-168 AD) |
100 BC |
Meeus 0 |
Meeus 2000 |
|
|
|
vernal
equinox - summer solstice |
|
|
93.96 d | 92.76 d |
|
|
summer
solstice - autumnal equinox |
|
|
92.45 d |
93.65 d |
|
|
autumnal
equinox - winter solstice |
|
|
88.69 d |
89.84 d |
| Winter | winter
solstice - vernal equinox |
90 1/8 d | 90.07 d | 90.13 d |
88.99 d |
| Sum | 365
1/4 d |
365.24 d | 365.23 d | 365.24 d |
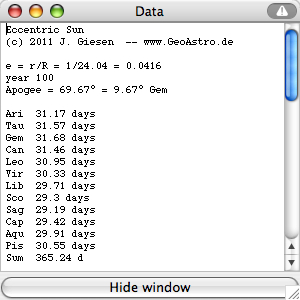
The
rounded
number
of days in zodiac signs agree with those of Geminus:
| Ari | Tau | Gem | Can | Leo |
Vir | Lib | Sco | Sag | Cap | Aqu | Pis | ||
| days | 31 | 32 | 32 | 31 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 365 |
| days | 95 | 92 | 88 | 90 | 365 | ||||||||
|
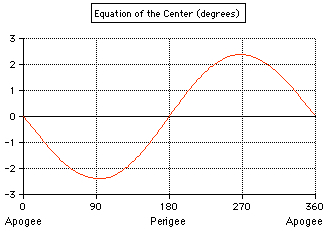
The equation of the center
(EoC) is the difference between the actual position of the Sun and the
position it would have if its angular motion were
uniform. maxEoC = arcsin(e)
e=1/24.0 maxEoC = 2° 23.3'
e=1/24.1 maxEoC = 2° 22.7' e=1/24.04 maxEoC = 2° 23.0' Ptolemy: In the appendix 2 "Calculation of the Eccentric-Quotient for the Sun" of Thurston's book, e is computed to be 143/3438 = 24.04, using the lengths of the seasons and 365 d 14/60 h 48/3600 min = 365.2467 d for the length of the tropical year given by Ptolemy. |
|
|
|
Hipparchus:
Orbit of the Sun (Wikipedia) Gemini Elementa Astronomiae, editit C.
Manitius (PDF, Greek/German) Des Claudius Ptolemäus Handbuch der
Astronomie (Übers. Karl Manitius) |
| Books |
| James Evans: The History and Practice of
Ancient Astronomy, Oxford University Press, 1998, Chapter Five: Solar Theory. Hugh Thurston: Early Astronomy, Springer, Berlin, New York 1994. Jean Meeus: Astronomical Tables of the Sun, Moon and Planets. 2nd ed., Willmann-Bell, Richmond 1995. Gemini Elementa Astronomiae, editit C. Manitius (Greek/German), Teubner, Stuttgart 1974. |
Updated:
2023, Oct 07